Resistance to steam sterilization is an important consideration for the selection of polymeric adhesives, sealants and potting compounds for use in medical applications. Autoclaving is one of the most rigorous and widely employed sterilization methods for medical devices. With this in mind, Master Bond has developed a wide variety of products for this purpose. Many compounds have been successfully tested for the U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP) Class VI requirements, and some select systems among them can withstand repeated autoclaving exposure1.
The following graphs display the autoclave resistance of many diverse Master Bond products. The products were cast into molds to create a size roughly of 2 inches in diameter, and 0.125 inches thick. These castings were then subjected to multiple autoclaving cycles up to 100 cycles. Each autoclave cycle was around 20 minutes at 250 F (~ 121°C) and about 15 psi of steam pressure. The weight change was then measured periodically, which is illustrated in the graph. As shown in the graphs below, there is a reference epoxy2, which gains much more weight compared to the other epoxies below, which have far superior resistance to weight gain.
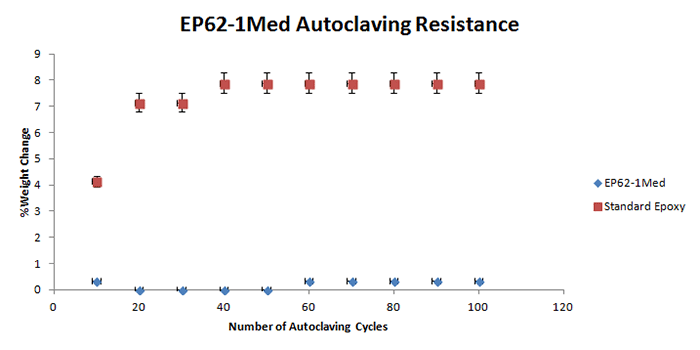
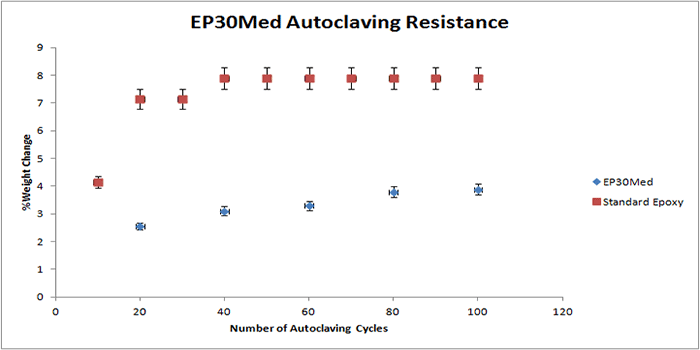
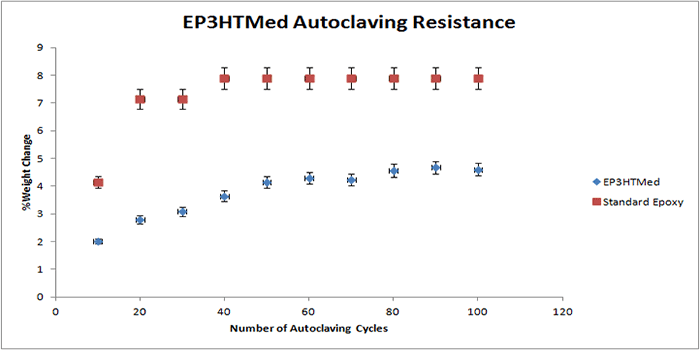
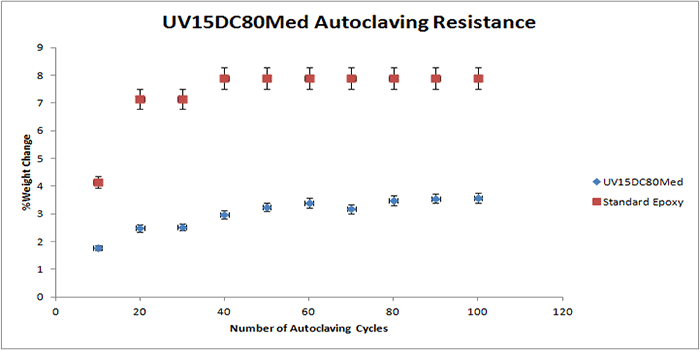
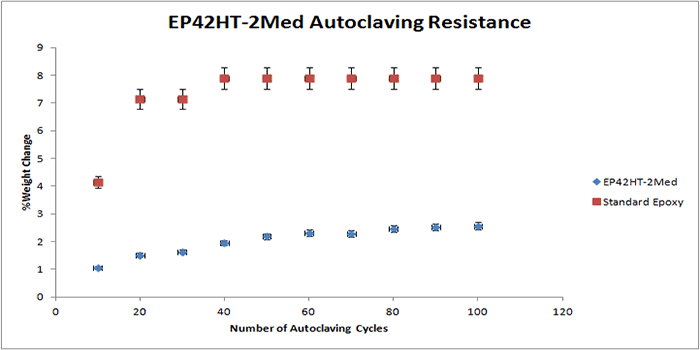
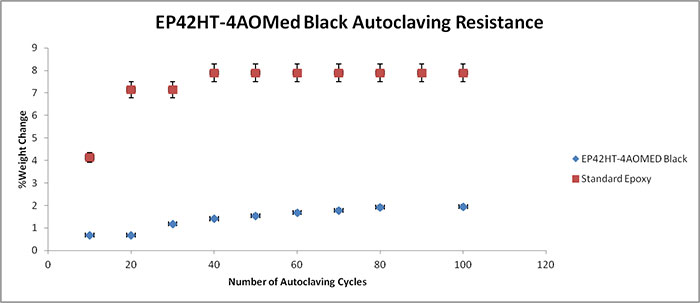
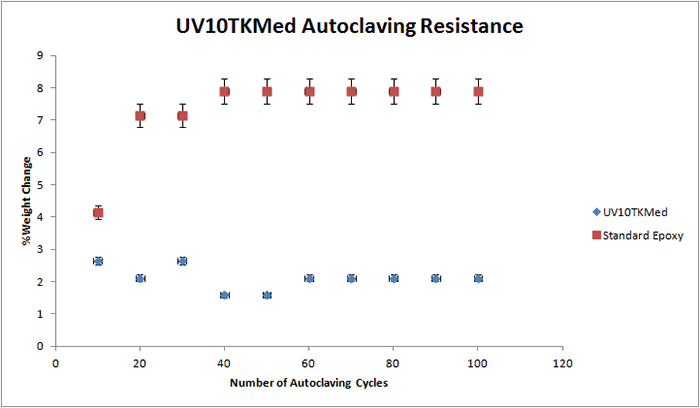
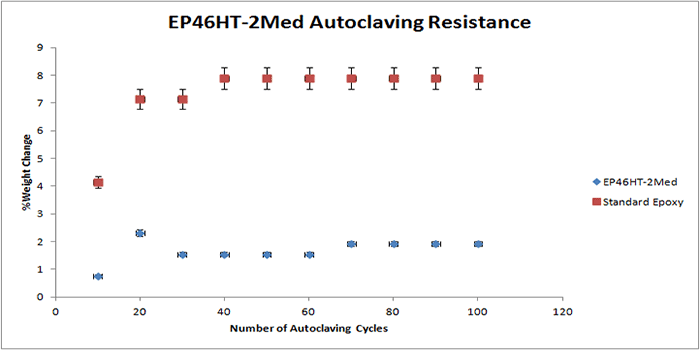
It must be noted that in selecting the right product for repeated autoclaving in your medical device, there are many other factors involved. For more information on Master Bond products, please contact our technical advisors.
Disclaimer: The findings in this article are not meant to be used for specification purposes.
1 The pass criteria was established as less than +/-5 % by weight.
2 Reference or standard epoxy used was EP21 (with a 4:5 mix ratio by weight).
Adhesives for Autoclave Resistance
 |
EP62-1Med Two part epoxy requiring moderate heat curing (80-120°C). Meets USP Class VI biocompatibility specifications. Superb resistance to repeated autoclaving along with excellent adhesion to high temperature plastics such as Ultem, PEEK, etc. Exceptionally long working life. Outstanding electrical insulation properties. Serviceable from -60°F to +450°F. |
 |
EP30Med Biocompatible two component epoxy. USP Class VI approved. Low viscosity. Versatile cure schedules. Resists EtO, gamma radiation and cold sterilants. High strength rigid bonds. Serviceable from -60°F to +250°F. Can be used for indirect food contact per 175.105 FDA specification. |
 |
UV15DC80Med USP Class VI approved one component UV and heat curable epoxy. Passes ISO 10993-5 cytotoxicity testing. Cures at temperatures as low as 80°C. Moderate viscosity. Minimal shrinkage upon cure. Capable of withstanding liquid sterilants, radiation, autoclaving. Serviceable from -60°F to +400°F. |
 |
EP42HT-2Med Low viscosity, two part epoxy with outstanding chemical resistance. Passes USP Class VI biocompatibility tests. Capable of withstanding repeated sterilization cycles including radiation, EtO, chemical sterilants, autoclaving. Serviceable from -60°F to +450°F. Cures at room or elevated temperatures. Available in amber-clear and black colors. Castable in thicknesses up to 2-3 inches. |
 |
UV10TKMed Biocompatible, high viscosity, UV curable compound. Optically clear. Glass transition temperature of more than 140°C. Rapid curing, no mix system. Withstands repeated sterilization. Meets USP Class VI and ISO 10993-5 cytotoxicity testing requirements. Serviceable from -60°F to +450°F. |
 |
EP46HT-2Med USP Class IV approved, heat resistant epoxy adhesive. Glass transition temperature in excess of 220°C. Withstands repeated exposure to autoclaving, radiation and chemical sterilants. High bond strength. Superior durability. Serviceable from -100°F to +500°F. Electrically insulative SUitable for potting. |
 |
EP3HTMed Rapid curing, one part epoxy. Meets USP Class VI biocompatibility standards. Thixotropic paste viscosity. High shear strength. Superb resistance to autoclaving, chemical sterilants, radition, EtO. Serviceable from -60°F to +400°F. |
 |
EP42HT-4AOMed Black Thermally conductive, electrically insulative two part epoxy. Meets USP Class VI and ISO 10993-5 certifications. Cryogenically serviceable from 4K to +400F. NASA low outgassing aproved. Black in color. For bonding, sealing, coating and casting. |
