Master Bond's thermally conductive adhesives offer superior heat dissipation for a wide range of electronic applications. Both one and two component systems are available for use. They include rigid and flexible adhesives and sealants for thermal management. Special thermal interface materials designed for unusual service conditions are also available.
Formulating Thermally Conductive Compounds
Thermal conductivity of a typical unfilled epoxy system has a very low value of 0.14 W/(m•K). This key property can be increased by adding metallic or ceramic fillers to the adhesive formulation. The type of filler, concentration of particles, their size and shape will determine the thermal conductivity of the product. They can be either electrically conductive or electrically insulative, as illustrated in the diagram below.
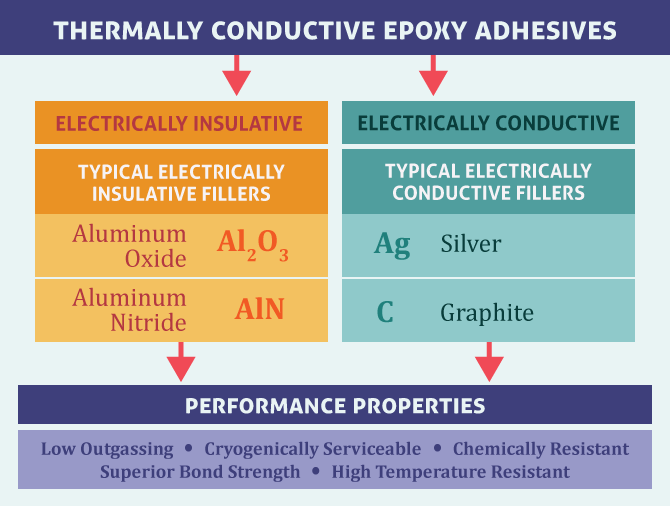
The chart below illustrates thermal conductivity values that can be achieved for select grades of systems with different fillers:
| System Type | Product | Filler | Thermal Conductivity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Two part epoxy | EP21TCHT-1 | Aluminum Oxide | >1 W/(m•K) |
| One part epoxy | EP5TC-80 | Aluminum Nitride | 3.3-3.7 W/(m•K) |
| One part epoxy | EP3HTS-TC | Silver | 16-17 W/(m•K) |
| Two part epoxy | EP75-1 | Graphite | 1.87-2.02 W/(m•K) |
Key factors influencing heat dissipation effectiveness
Master Bond thermal interface materials (TIMs) are often applied between heat generating electronic components and cooling devices such as heat sinks. These systems are compounded to fill in thermally insulative air gaps, maximize heat transfer efficiency, improve device reliability and extend longevity. The following factors minimize the thermal resistance:
- High thermal conductivity
- Minimal bond line thickness
- Complete polymerization
- Elimination of voids
Thin Bonds Maximize Heat Transfer Properties
The lower the thermal resistance, the better the heat transfer. In this regard, Master Bond utilizes the principles based on the formula:
R=t/K
(where “R” is the thermal resistance; “t”, the thickness and “K” the thermal conductivity of the material). Master Bond epoxy thermal interface materials feature ultra thin bond lines to improve heat transfer characteristics. Thicknesses as small as 10-15 microns can be achievable using some compounds.
Common Applications Featuring Thermally Conductive Adhesives
Thermally conductive formulations are used for bonding, coating, potting and encapsulation applications in a wide variety of industries. Some specific applications include:
- Heat sink bonding
- Potting/encapsulating sensors
- BGA die heat spreader interface
- Chip scale packages
- Power semiconductors
Master Bond thermally conductive adhesives offer convenient room temperature or heat cure schedules in controlled production environments. Many systems withstand 1,000 hours at 85°C/85% RH. They can be serviceable in a wide range of temperatures from 4K to over 500°F. Specific systems are designed to offer superior dimensional stability, adhere well to substrates with dissimilar coefficients of thermal expansion and resist vibration, impact, shock. They can be dispensed manually or automatically. Select two component grades are available for use in premixed and frozen syringes.
Our Most Popular Thermally Conductive Adhesive Formulations
 |
EP3HTS-TC Silver filled electrically conductive, for die attach and general bonding. Low volume resistivity and high temperature resistance. Superior bond strength. Thermally conductive. Thixotropic paste, consistency. Available in syringes that are compatible with various types of automatic dispensers or manual dispensing. Serviceable from -80°F to +400°F. |
 |
EP40TCMed Flexible, moderate viscosity bonding, potting, sealing, encapsulation compound. High shear/peel strength. Easy processing, high elongation, biocompatible. Serviceable from -100°F to +300°F. |
 |
EP3HTSDA-2 Silver filled electrically conductive epoxy has a rapid cure speed. Low volume resistivity and high temperature resistance. Superior bond strength. Thermally conductive with incredibly low thermal resistance. Smooth paste, consistency. Available in syringes that are compatible with various types of automatic dispensers or manual dispensing. Serviceable from -80°F to +450°F. |
 |
EP30NG Graphene filled epoxy. Non-drip system for bonding and sealing. Cures at room temperature. Superior abrasion resistance. |
 |
MasterSil 705TC Thermally conductive and electrically isolating. Easy to use silicone for high performance bonding, sealing and coating. Non-corrosive and room temperature curable. Ideally suited for applications requiring flexibility and high temperature resistance. |
 |
EP5G-80 Graphite filled epoxy that cures at 80°C. Good electrical and thermal conductivity. Passes NASA low outgassing certification. Can be used for bonding, sealing, coating. Service temperature range is -50°C to +175°C |
 |
EP29LPAOHT Two component epoxy system featuring good thermal conductivity along with being electrically isolating. It is a low to moderate viscosity system with excellent flow properties. It can be mixed in masses over a gallon because it generates an exceptionally low exotherm. High modulus, outstanding compressive strength, and a low coefficient of thermal expansion. The service temperature range is -60°F to +350°F. |
 |
EP35AOLV Thermally conductive, electrically isolating epoxy serviceable from -60°F to +500°F. Heat curing, good flow. Superior chemical resistance properties. Long pot life. High compressive strength and dimensionally stable. |
 |
EP40TC Flexible, moderate viscosity bonding, potting, sealing, encapsulation compound. High shear/peel strength. Easy processing, high elongation, vacuum compatible. Serviceable from -100°F to +300°F. |
 |
MasterSil 153AO Thermally conductive silicone casting, potting and sealing system. Thermal conductivity of 0.35-.0.54 W/(m•K). Electrically isolating. Low viscosity system bonds well to a wide variety of substrates. Remarkable flexibility. Temperature resistant from -65°F to +400°F. White color. |
